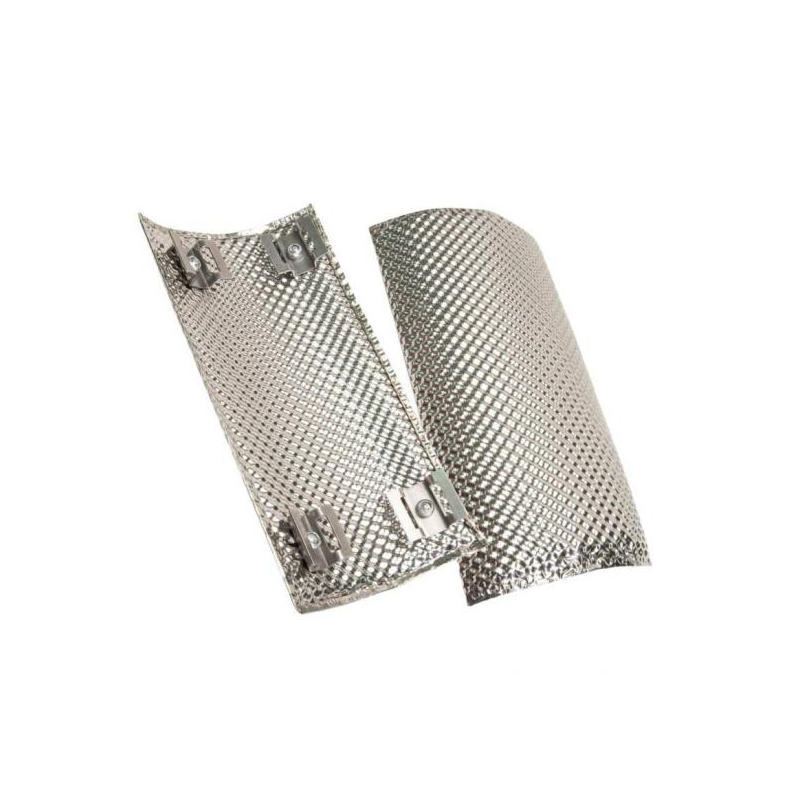
Exhaust heat shield is a protective component designed to shield surrounding parts of a vehicle or machinery from the high temperatures generated by the exhaust system. Made from materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, or heat-resistant composites, exhaust heat shields help to reduce the risk of heat damage to nearby components like hoses, wires, and fuel lines. They are commonly used in automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications where controlling heat is critical for safety and performance. By directing and dissipating heat away from sensitive areas, these shields improve the longevity and efficiency of the vehicle or machinery. Designed for durability, exhaust heat shields are resistant to high temperatures, corrosion, and physical wear, making them an essential component for ensuring the safe operation of exhaust systems.
Basic Information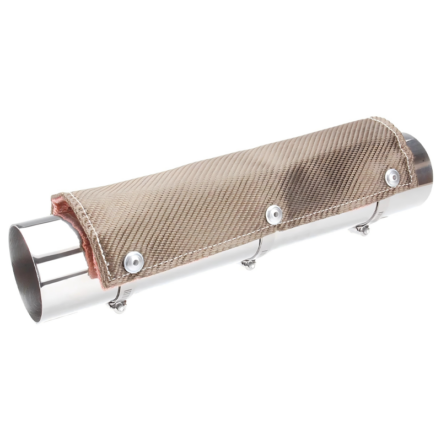
– Surface Treatment: Electroplating
– Forming Process: Metal Stamping Parts
– Surface Finish Options: Nickel Plating, Sn Plating, Tin Plating, Zinc Plating
– Sample Availability: Available
– Tolerance: ±0.001 mm
– Size: Customizable as per requirement
– Application: Industrial, Furniture, Automotive, Motorcycle, etc.
– Manufacturing Approach: Metal Stamping, Cutting, Punching, Bending, Welding
– Transport Packaging: OPP Bag, Box, or Custom
– Specification: Customized
– Origin: Xiamen, China
Surface Treatments for Metal Stamping Parts
-
Electroplating
– Description: A process that deposits a layer of metal onto the surface of the part using an electric current. Commonly used for improving corrosion resistance and enhancing appearance.
– Types: Nickel plating, chrome plating, zinc plating.
-
Powder Coating
– Description: A dry coating process where powdered paint is electrostatically applied and then cured under heat. It provides a durable, high-quality finish with excellent resistance to scratches, chipping, and fading.
-
Anodizing
– Description: An electrochemical process that converts the surface of aluminum into a durable, corrosion-resistant layer. Anodizing also enhances appearance and can be dyed in various colors.
-
Plating
– Description: The application of a thin layer of metal to the surface of the part to improve wear resistance, reduce friction, or provide an aesthetic finish.
– Types: Tin plating, copper plating.
-
Spraying
– Description: A method where paint or protective coating is sprayed onto the part’s surface. This process is used for both aesthetic and protective purposes, offering a wide range of colors and finishes.
-
Oxidation
– Description: A chemical treatment that forms a protective oxide layer on the surface of metals, such as steel. It improves corrosion resistance and can provide a unique aesthetic finish.
-
Polishing
– Description: A mechanical process that smooths and shines the surface of the part. Polishing removes imperfections and enhances the visual appeal of the metal.
-
Sandblasting
– Description: A process that uses high-speed abrasive particles to clean or roughen the surface. It prepares the surface for further treatments or provides a textured finish.
-
Passivation
– Description: A treatment process that enhances the natural oxide layer on stainless steel to improve corrosion resistance. It involves soaking the part in a solution that removes free iron and other contaminants.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.