When it comes to joining metal components, selecting the right method is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, structural integrity, and longevity. Among the most common joining techniques are welding and riveting. Each method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to carefully evaluate the specific needs of your project. At Topmetalstamping, we specialize in providing high-quality metal stamping and joining solutions, helping you choose the most suitable method for your manufacturing requirements. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between welding and riveting, highlighting the pros and cons of each technique to help you make an informed decision.
What is Welding?
Welding is a thermal process used to join two or more metal parts by melting the surfaces and allowing them to fuse together, often with the addition of a filler material. It is one of the most reliable and permanent joining techniques, offering strong and durable connections. Welding is typically used in applications requiring high strength, such as in the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries. There are several different types of welding, including arc welding, MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, and laser welding. Each method has specific advantages depending on the materials being joined and the precision required.
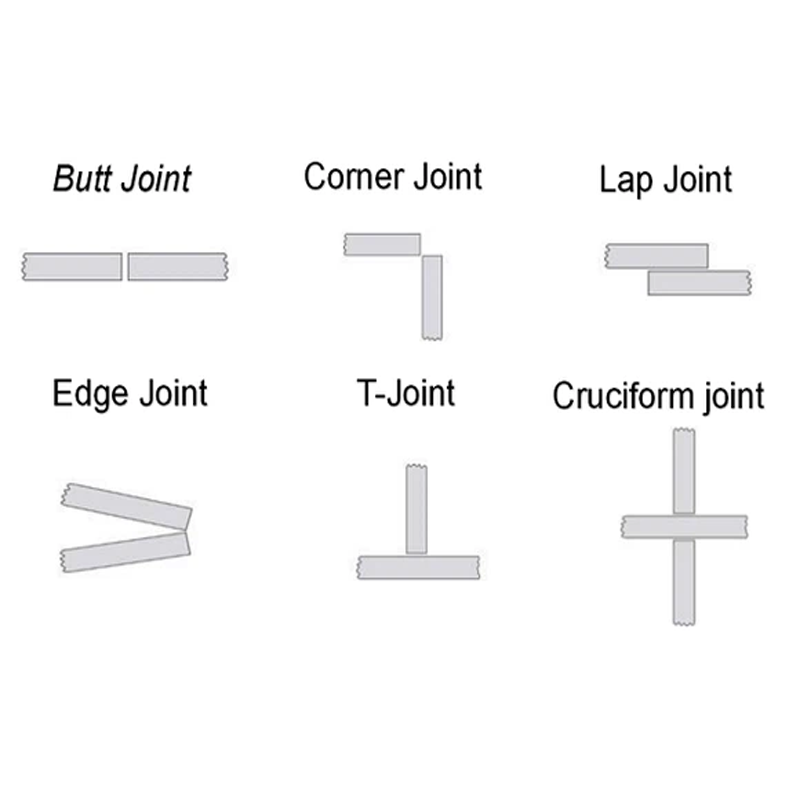
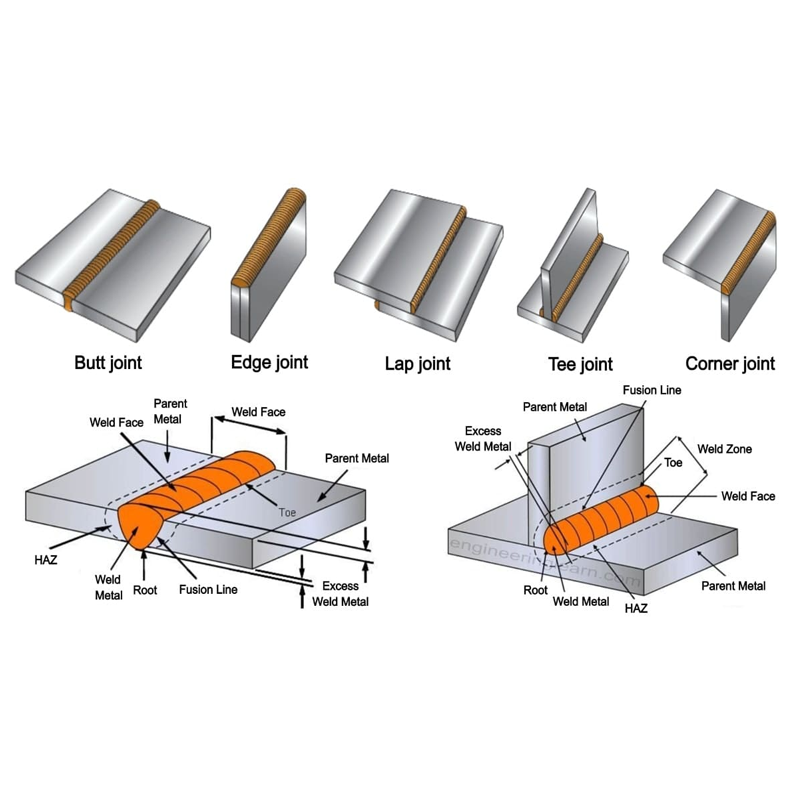
Types of Welding Joints:
- Butt Joint: Metal parts are aligned on the same plane, and the edges are welded together.
- Lap Joint: Metal parts partially overlap and are welded at the overlapping section.
- Corner Joint: Two metal parts meet at a right angle, typically forming a corner or frame.
- T-Joint: One metal component intersects laterally with another to form a “T” shape.
- Edge Joint: Used to join the edges of parts, typically at an angle of 30° or less.
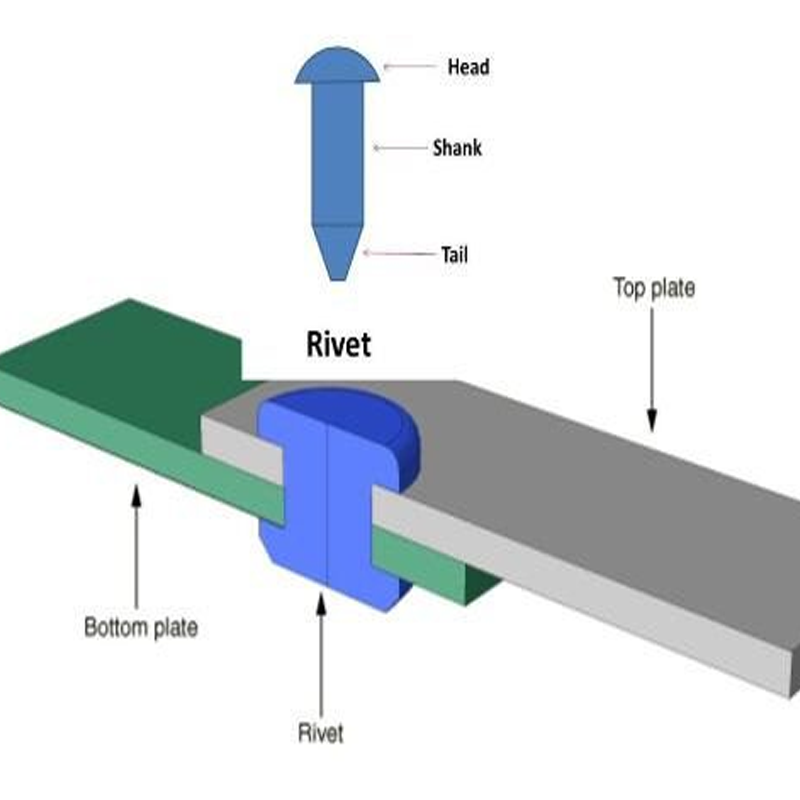
What is Riveting?
Riveting, on the other hand, is a mechanical process in which rivets are used to join metal parts. Riveting involves inserting a rivet through pre-drilled holes in the components and then deforming the rivet’s ends to secure the parts together. Unlike welding, which requires high heat, riveting is a cold-process method that can be performed at ambient temperatures, making it suitable for a broader range of materials, including those sensitive to heat.
Riveting is a versatile technique often used in applications where heat could damage the material or when a non-permanent, flexible connection is desired. It’s commonly used in the aerospace, automotive, and construction industries, particularly for joining sheet metal and structures that need to withstand vibrations and dynamic loads.
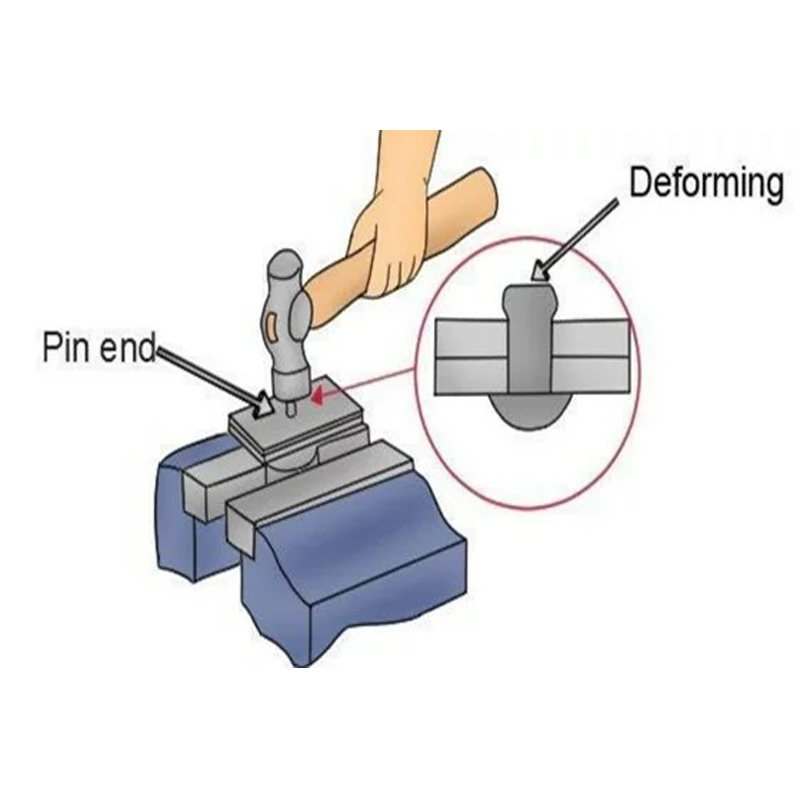
Types of Rivet Joints:
- Lap Joint: Rivets are used to join two overlapping pieces.
- Butt Joint: The ends of two pieces are butted together and riveted.
- Single Riveted Lap Joint: Uses a single row of rivets to join overlapping pieces.
- Double Riveted Lap Joint: Uses two rows of rivets for enhanced strength.
- Staggered Rivet Joint: Rivets are arranged in a staggered pattern to improve strength and distribute the load more evenly.
Key Differences Between Welding and Riveting
Understanding the key differences between welding and riveting can help you determine which method is best suited for your specific application. Let’s break down some of the major considerations:
1. Joining Mechanism:
- Welding: This process melts the workpieces and fuses them into a single solid unit. The welded joint becomes an integral part of the metal, making the connection permanent.
- Riveting: Riveting uses mechanical pressure to insert rivets into the workpieces, forming a point connection without permanently altering the material. The joint remains flexible and can be disassembled if needed.
2. Temperature:
- Welding: Requires high temperatures to melt and fuse the material, making it unsuitable for heat-sensitive metals or coatings.
- Riveting: Operates at room temperature, making it ideal for materials that could be damaged by heat, such as certain plastics, coated metals, or sensitive alloys.
3. Strength and Durability:
- Welding: Provides a strong, permanent bond that can withstand high stresses and extreme conditions, making it ideal for structural components that require maximum strength.
- Riveting: Riveted joints are typically more flexible and may not offer the same level of strength as welded connections. However, they are still highly effective for many applications, particularly when the materials are subject to vibration or dynamic loads.
4. Process Time:
- Welding: Generally involves a more time-consuming process with extensive preparation and post-welding treatments. The welding process can be slower, especially for thicker materials or larger projects.
- Riveting: Riveting is a faster process, especially when automated systems are used. It requires less preparation, making it an efficient choice for high-volume production.
5. Aesthetic Considerations:
- Welding: The finished welded joint can be smoothed out, offering a cleaner, more seamless appearance. The surface can be ground or polished to improve the visual quality of the product.
- Riveting: Rivets are visible on the surface, and even countersunk rivets may protrude slightly, giving the joint a more industrial look. This may be less desirable for applications requiring a sleek, clean appearance.
6. Leak-Proofing and Sealing:
- Welding: Provides a tight, leak-proof seal, making it ideal for applications that require fluid or gas containment.
- Riveting: While riveting offers a secure joint, small gaps around the rivet heads may make it less suitable for applications that require airtight or watertight seals.
Choosing Between Welding and Riveting
When it comes time to decide between welding and riveting, several factors must be considered:
- Material Type: Welding is not always suitable for every material. For example, certain alloys, composites, or heat-sensitive materials may deform or degrade under the heat required for welding. In such cases, riveting would be the better option.
- Strength Requirements: For high-stress applications where maximum strength is crucial, welding is typically the preferred choice due to its ability to provide a strong, monolithic bond. However, for components that experience repeated stress or need to be dismantled, riveting may offer a better solution.
- Speed and Volume: If you’re working on a high-volume production line where speed is essential, riveting—especially when automated—can provide quicker assembly. Welding, on the other hand, may slow down the production process due to its more complex nature.
- Cost and Efficiency: Riveting tends to be a more cost-effective solution, especially when it comes to simpler projects or where less precision is required. Welding, with its equipment and process complexity, can be more expensive in terms of both material and labor.

Welding and Riveting | How to Choose?
In summary, both welding and riveting offer distinct advantages and limitations depending on the nature of your project. Welding is the go-to method when you require high-strength, permanent, and seamless joints, especially for heavy-duty applications. On the other hand, riveting excels in situations where flexibility, speed, and non-permanent connections are required, or when dealing with materials sensitive to heat.
At Topmetalstamping, we specialize in offering both welding and riveting solutions to meet the diverse needs of our clients. Our team of experts can guide you in selecting the best method based on your materials, design, and performance requirements. Whether you’re working on a complex automotive project, constructing large metal structures, or creating components for precision industries, we are here to ensure that your joining needs are met with the utmost efficiency and quality.
Conclusion
Choosing the right joining method—welding or riveting—depends on several key factors, including the materials involved, the strength required, aesthetic considerations, and production speed. At Topmetalstamping, we understand the intricacies of both techniques and are committed to helping you find the optimal solution for your project. With our expertise in both welding and riveting, you can trust that your parts will be joined securely, efficiently, and with precision.
If you’re unsure which method is best for your needs, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at Topmetalstamping. Our team is ready to provide a professional consultation and help you choose the most suitable joining technique for your specific requirements. Let us guide you to a stronger, more durable solution for your metal fabrication projects.



