Have you ever wondered how to enhance the durability and corrosion resistance of your metal parts while maintaining an affordable budget? Black oxide coating could be the solution you’re seeking. This process provides an effective shield against rust and wear, extending the lifespan of your components. At Topmetalstamping, we specialize in offering high-quality black oxide coating services that cater to a variety of industries and applications. In this blog, we’ll delve into the various types, advantages, applications, and testing methods of black oxide coating to help you make informed decisions for your metal components.
What is Black Oxide Coating?
Black oxide coating is a thin protective layer applied to ferrous metals like steel, stainless steel, and cast iron. This layer is formed through a chemical process that turns the metal surface into a black iron oxide known as magnetite (Fe3O4). Though commonly applied to ferrous metals, the process can also be used on select non-ferrous metals, including copper, brass, zinc, and aluminum.
One of the unique features of black oxide coating is that it doesn’t add thickness to the material like other coatings (e.g., plating or painting). Instead, it transforms the surface, offering a sleek, matte black finish that enhances both functionality and aesthetics. Also referred to as blackening, gun bluing, or black passivating, black oxide coating plays a vital role in providing corrosion resistance and reducing wear on metal surfaces.

When Should Black Oxide Coating Be Used?
Black oxide coating is primarily used to improve the corrosion and wear resistance of ferrous metals. A key advantage of this process is the minimal buildup it creates on the metal’s surface. Unlike other coatings, which may significantly increase the thickness of the material, black oxide coating adds only a thin layer, typically no more than 0.000020 inches. This minimal buildup ensures that the dimensional integrity of high-precision components is preserved.
The black oxide coating is ideal for applications where durability, corrosion resistance, and an enhanced appearance are critical. It is commonly found in industries like automotive, firearms, precision tools, and decorative components. Furthermore, the coating provides a matte finish that doesn’t fade over time, unlike other more affordable finishes that may wear away quickly.
Materials That Can Be Coated with Black Oxide
Black oxide coating is compatible with a wide range of materials. Here’s a breakdown of the metals that can be treated:
– Ferrous Metals: Black oxide coating works best on ferrous metals such as:
– Alloy steel and carbon steel
– Cast iron
– Stainless steel
– Non-ferrous Metals: Although the process is primarily used for ferrous metals, it can also be applied to certain non-ferrous materials. However, the process for non-ferrous metals requires additional steps, such as electrochemical treatment, to achieve the desired black oxide finish. Common non-ferrous metals that can be treated include:

– Copper and brass
– Zinc
– Aluminum
Types of Black Oxide Coating
There are several black oxide coating methods, each suited for different applications and environmental considerations. Here are the main types:
- Hot Black Oxide: This is the most common method used in industries such as firearms and automotive manufacturing. The metal is submerged in a hot bath containing sodium hydroxide, nitrates, and nitrites at temperatures ranging from 285°F to 295°F. This process creates a durable, black magnetite layer that enhances corrosion resistance and wear protection.
- Cold Black Oxide: Ideal for applications where heating is not feasible, the cold black oxide process involves applying a solution of selenium, copper, and phosphoric acid at room temperature. This method is particularly suited for quick, aesthetic-focused applications, though it doesn’t offer long-term durability compared to hot black oxide.
- Mid-Temperature Black Oxide: This method operates at a lower temperature range (220°F to 245°F) and uses safer, more environmentally friendly chemicals. It provides a balanced approach, offering excellent corrosion resistance while reducing energy consumption and ensuring minimal dimensional impact.

Step-by-Step Process for Black Oxide Coating
The process for applying black oxide coating may vary depending on the method chosen. Below, we outline the steps for the hot black oxide process, which is the most commonly used method:
- Cleaning the Surface: The first step is to thoroughly clean the metal surface to remove oils, grease, rust, and other contaminants. Alkaline detergents are commonly used for this purpose, ensuring that the surface is free of debris.
- Rinsing: After cleaning, the metal is rinsed in water to remove any detergent residues.
- Acid Pickling: This step removes any rust stains or oxide films from the metal surface. Acid pickling is typically performed using an acidic solution.
- Rinsing Again: The metal is rinsed once more to remove any acid residue.
- Chemical Bath: The metal is then dipped into a hot bath containing a mixture of nitrites, nitrates, and caustic soda. This process forms the black iron oxide layer (Fe3O4) on the metal surface.
- Rinsing: After achieving the desired black oxide finish, the metal is rinsed again to remove any compound residues.
- Sealing: The final step involves applying a sealant, such as oil or wax, to seal the metal’s surface. This protects the coating and enhances its appearance. For a matte finish, clear wax is used instead of oil.
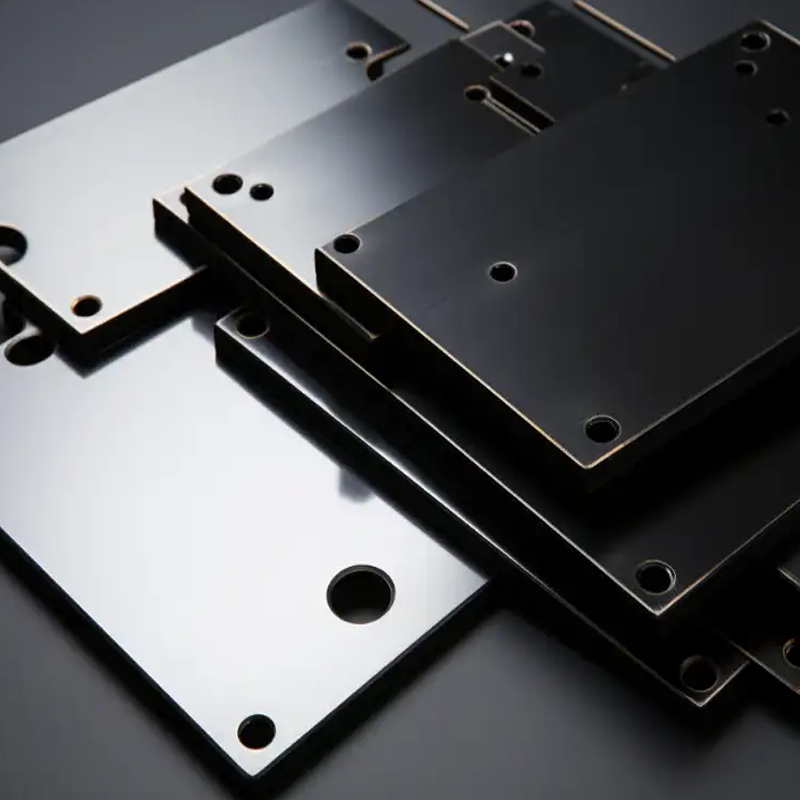

Advantages and Disadvantages of Black Oxide Coating
Black oxide coating offers several benefits but also has a few limitations:
Benefits:
– Cost-Effective: Black oxide coating is a relatively inexpensive method compared to alternatives like electroplating, making it an affordable choice for many industries.
– Improved Appearance: The coating creates a uniform matte black finish that enhances the aesthetic appeal of metal parts.
– Corrosion Resistance: Black oxide coating provides excellent protection against rust and corrosion, ensuring longer-lasting performance.
– Lubricity: The coating helps improve lubrication between moving parts, reducing friction and wear.
– Minimal Dimensional Impact: The thin layer of black oxide coating ensures that the dimensional integrity of high-precision parts remains intact.
Drawbacks:
– Durability: While the coating improves corrosion resistance, it doesn’t offer the same level of durability as other coatings like electroplating. It may wear off over time, especially in harsh environments.
– Labor-Intensive: The black oxide coating process requires careful cleaning, acid pickling, and sealing, which can be labor-intensive and time-consuming.
Black Oxide Coating Applications
Black oxide coating is widely used across various industries. Its applications include:
– Firearms: The coating is commonly used on firearms to reduce glare and prevent corrosion, ensuring that the weapons perform reliably.
– Automotive: Black oxide coating is used on automotive components like bearings and gears to reduce friction and improve performance.
– Precision Tools: It is also applied to precision tools like lab instruments to reduce glare and ensure better focus.
– Decorative Applications: The aesthetic finish provided by black oxide coating makes it a popular choice for jewelry and other decorative metal products.
Testing Options for Black Oxide Coating
Several testing methods ensure the quality and effectiveness of black oxide coatings:
– Smut Test: This test helps identify any powdery residue left on the surface before sealing.
– Humidity Test: This test evaluates the corrosion resistance of the black oxide coating under humid conditions.
– Hardness Test: Measures the strength of the coating by pressing it with a durometer.
– Coating Thickness Assessment: Ensures the black oxide layer is of adequate thickness to provide proper protection.
– Salt Spray Test: This test evaluates the coating’s ability to resist corrosion when exposed to saltwater.

Conclusion:
In conclusion, black oxide coating is an effective, cost-efficient solution for enhancing the corrosion resistance and wear resistance of metal parts. While it offers several advantages, including improved appearance, lubrication, and minimal dimensional impact, it may not be suitable for all environments due to its moderate durability.
At Topmetalstamping, we provide high-quality black oxide coating services tailored to meet the specific needs of your project. Whether you need corrosion resistance for automotive parts, precision tools, or decorative applications, we ensure a high level of expertise and professionalism in every coating process. Contact us today to learn how black oxide coating can enhance your metal products and improve their performance!




