When it comes to building strong, reliable structures, metal brackets are essential components. From supporting heavy equipment to holding shelves in place, these versatile pieces play a pivotal role in countless applications. Whether you’re assembling furniture, constructing industrial machinery, or designing high-performance systems, selecting the right metal bracket is crucial for ensuring stability and longevity. At Topmetalstamping, we specialize in creating custom metal brackets designed to meet the specific needs of your projects, with a focus on quality and precision. This blog will provide an in-depth look at metal brackets—what they are, how they are made, the types available, and factors to consider when choosing the right bracket for your application.
What Is a Metal Bracket?
A metal bracket is a hardware component used to connect, support, or hold two or more objects or surfaces in place. Typically, metal brackets are used to strengthen structures by providing additional support, reinforcing joints, or securing equipment. They come in various shapes, such as L, T, U, and Z, each with a specific function depending on the application. These brackets are typically made from high-strength metals, ensuring that they are durable enough to withstand external forces like tension, pressure, and shear.
The most common method for creating metal brackets is sheet metal stamping. This process involves cutting and shaping a flat piece of metal into a desired bracket form. The result is a sturdy, reliable component that can be used in a variety of applications, ranging from shelving and furniture to industrial machinery and electrical equipment.
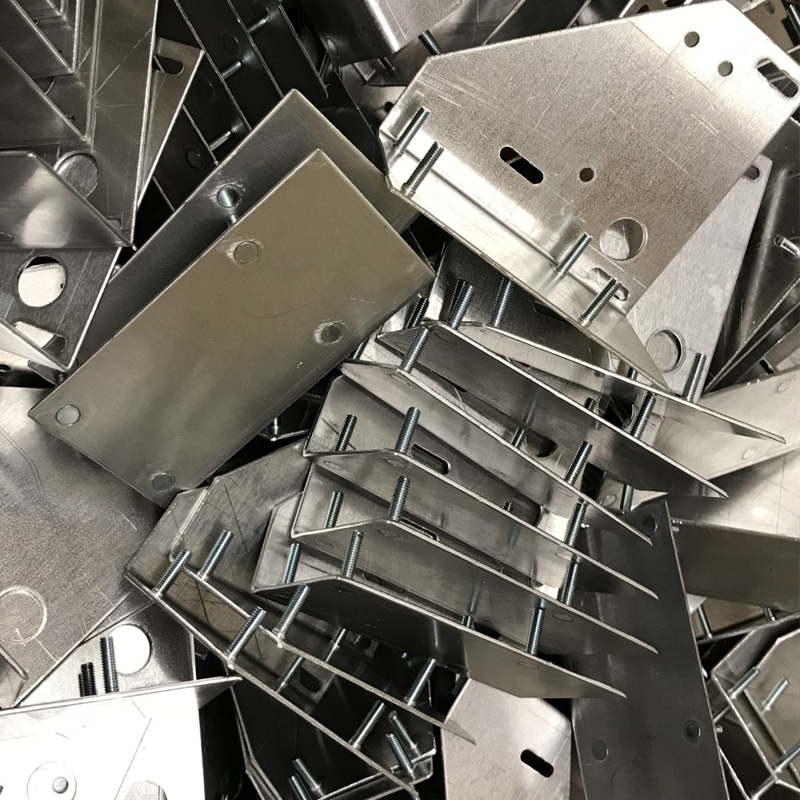

How Are Metal Brackets Made?
Metal brackets can be manufactured using a variety of methods, including casting, CNC machining, and sheet metal stamping. However, sheet metal stamping is often the most cost-effective and efficient method for producing simple and complex metal brackets alike.
Sheet Metal Stamping: This method involves using a die and a punch press to cut and form metal sheets into the required shape. The process allows for the mass production of metal brackets with high precision and consistency. A variety of cutting methods can be used in this process, including:
– Laser Cutting: Provides precise and intricate cuts, ideal for creating complex designs or small-scale projects.
– Stamping Press: A high-speed method that shapes metal sheets for large production runs, ideal for creating uniform brackets quickly and efficiently.
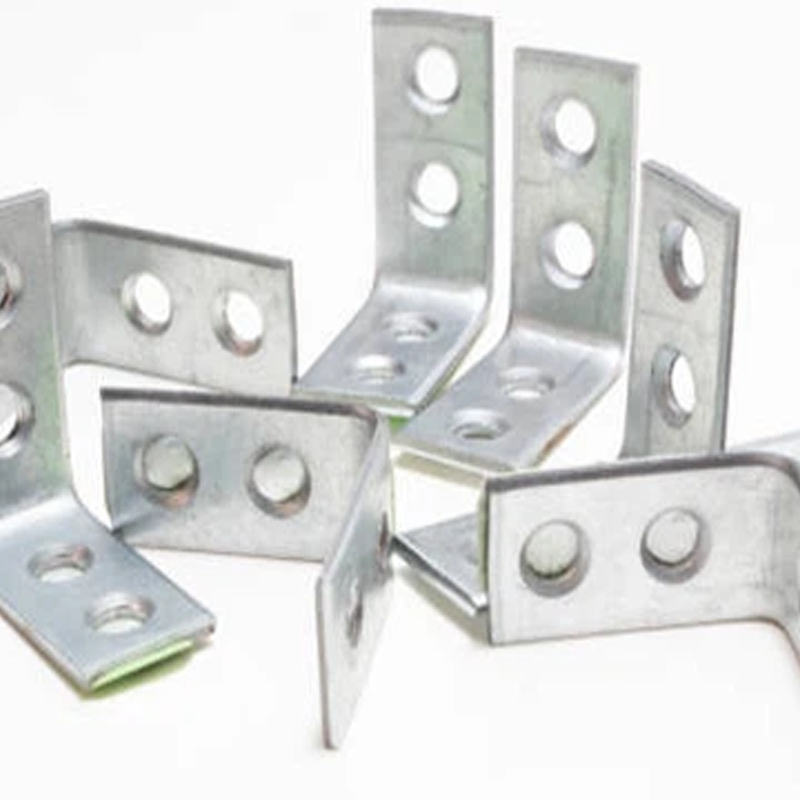

– Waterjet Cutting: Uses high-pressure water to cut metal, offering the ability to create precise shapes without heat distortion.
Once the metal is cut, it is bent into the desired shape using a press brake machine. This machine applies pressure to bend the metal along predefined angles, such as the standard 90° L-shape. For more complex brackets, welding may be required to join multiple pieces of metal together, ensuring a strong, durable structure.
Punching and Drilling: Many metal brackets also require holes to accommodate screws, bolts, or other fasteners. These holes are created through punching or drilling, allowing for easy attachment to other surfaces. Depending on the design, some holes may be threaded to enable secure tightening.
Types of Metal Brackets
Metal brackets come in a wide variety of shapes and configurations, each designed for a specific purpose. Below are some of the most commonly used types of metal brackets:
– L-Shaped Brackets: These brackets are typically used for corner joints, where two surfaces meet at a right angle. They are often found in furniture assembly, shelving units, and wall-mounted fixtures.

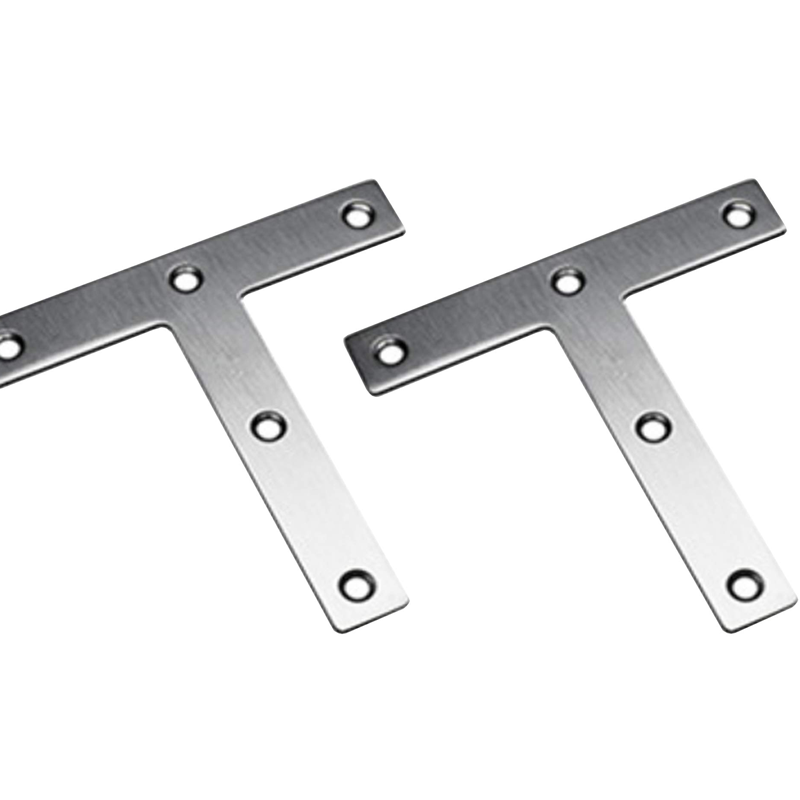
– T-Shaped Brackets: Resembling the letter T, these brackets are ideal for connecting three surfaces or components at a right angle. They are frequently used in complex frame structures and heavy-duty equipment.

– U-Shaped Brackets: With an upward bend on both sides, these brackets provide support for cylindrical objects such as pipes or tubes. They are commonly used for pipe supports, cable trays, and other round components.
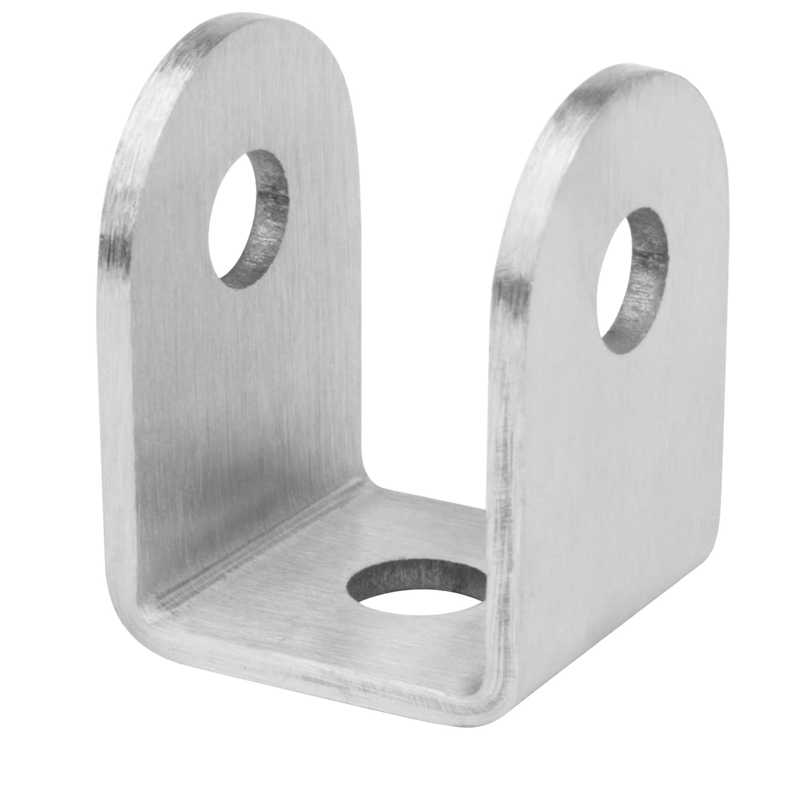

– Z-Shaped Brackets: These brackets are characterized by their Z-shape, offering multi-directional support. They are used in situations where multiple angles are needed, such as wall mounting or supporting furniture.
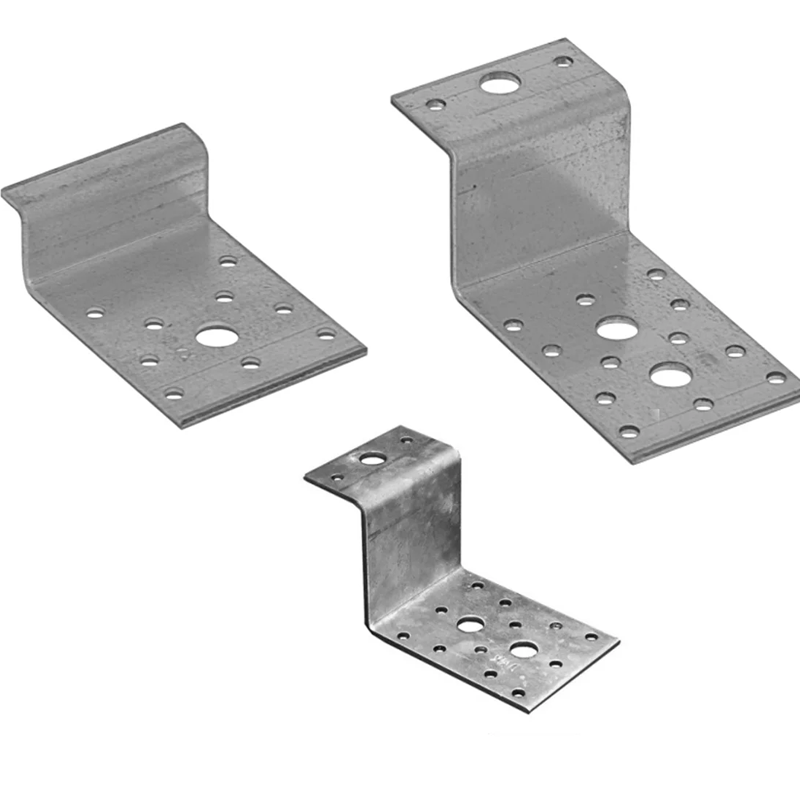

– H-Shaped Brackets: Designed to support larger structures, these brackets provide stability for large frame assemblies or industrial equipment.
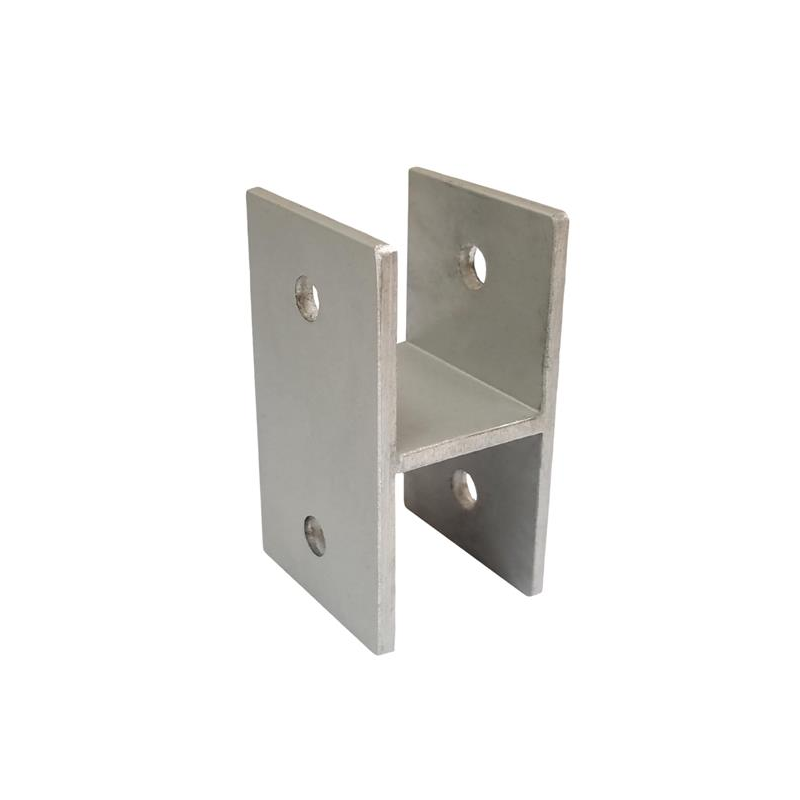

– Angle Brackets: Shaped like a triangle, these brackets offer extra reinforcement for corners or connection points. They are commonly used in furniture manufacturing and for equipment support.
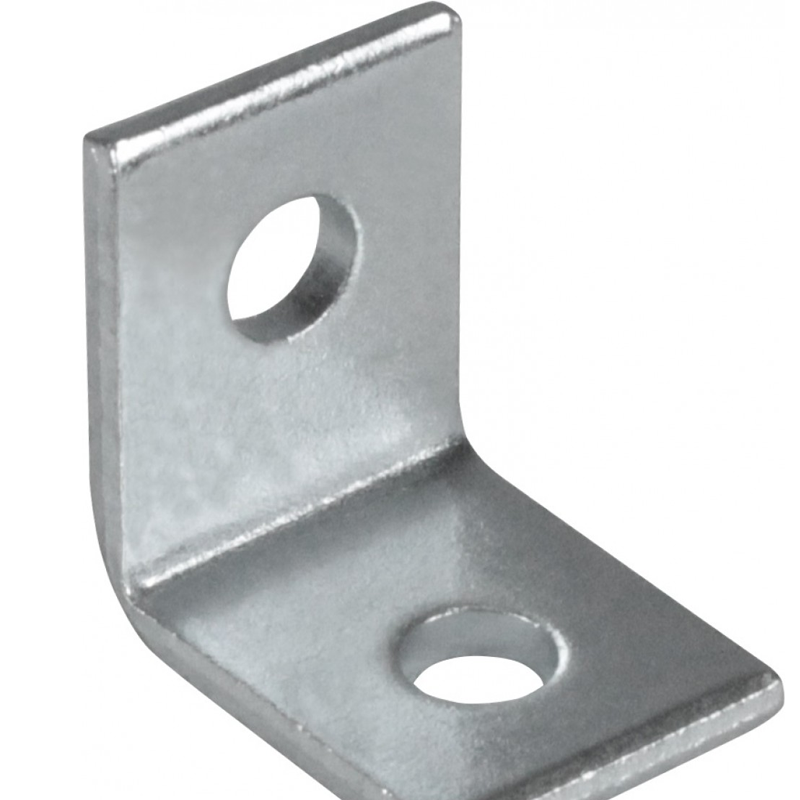

– Flat Brackets: Simple, flat brackets that are ideal for reinforcing surfaces or joining two objects together. These are typically used in light equipment support and furniture assembly.

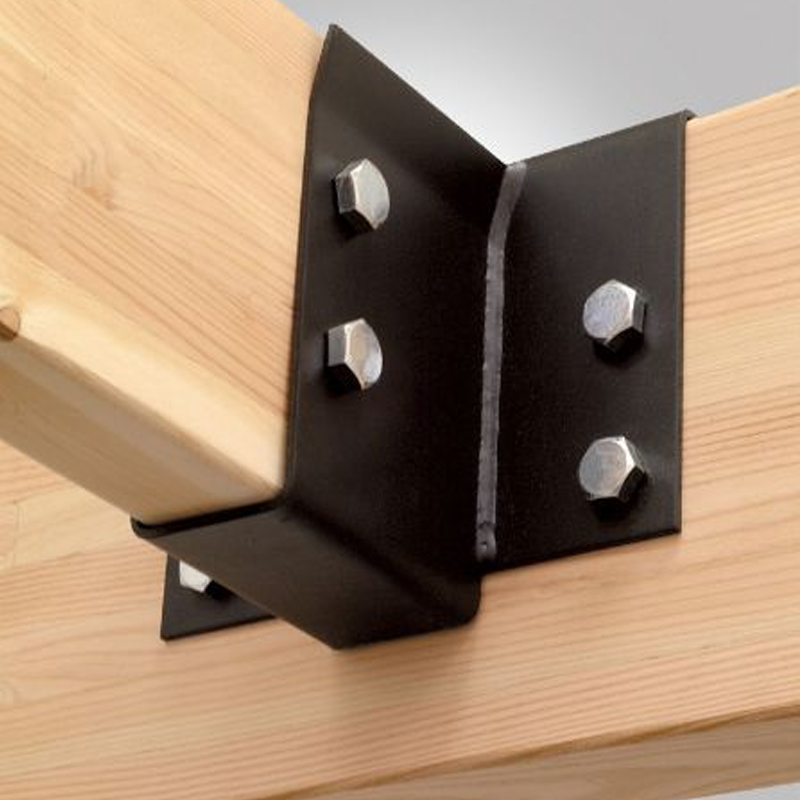
– Beam Hangers: Used primarily for shelving or hanging applications, these brackets provide support for beams, making them ideal for warehouse or industrial shelving systems.

Key Components of Metal Brackets
Regardless of their shape or function, most metal brackets share similar components that contribute to their overall strength and stability. These include:
– Base Plate: The flat or bent section of the bracket that attaches to the surface. The base plate provides stability and ensures that the bracket remains securely in place. Most base plates feature pre-drilled holes for easy attachment.
– Support Arm: Extending from the base plate, the support arm provides the structural support needed to hold objects in place. The size and design of the support arm vary depending on the bracket’s intended use.
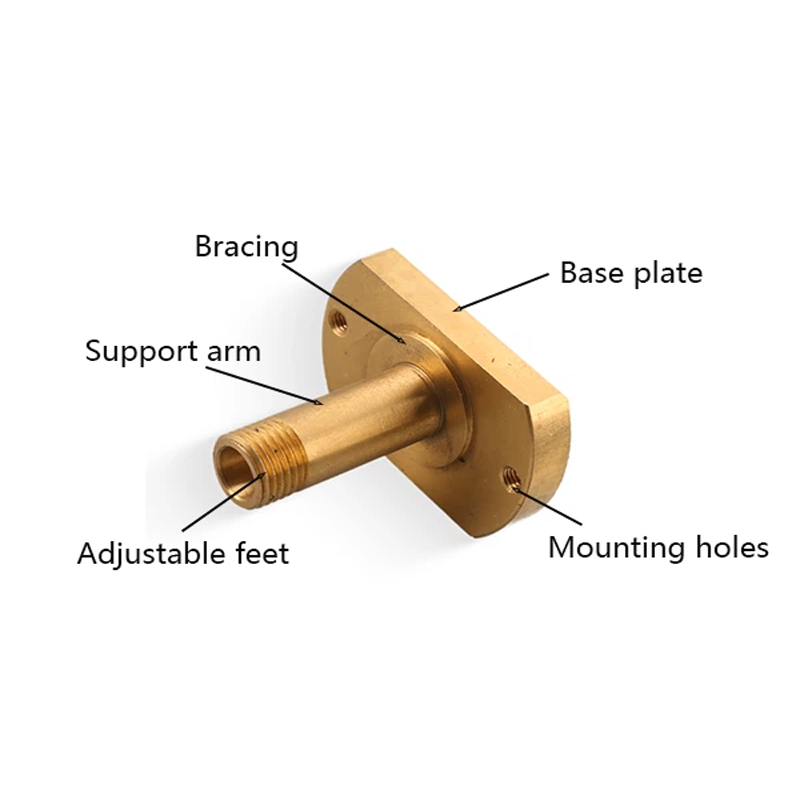
– Mounting Holes: Holes are punched or drilled into the bracket to allow it to be attached securely to other objects. These holes are sized and positioned based on the application.
– Bracing: Additional supports may be added to reinforce the bracket’s structure, providing increased strength and stability. Bracing ensures that the bracket can withstand heavy loads and resist bending or twisting.
– Adjustable Features: Some metal brackets come with adjustable elements, such as slots or holes, which allow for easy customization and alignment during installation.
Materials Used in Metal Brackets
The material used for manufacturing metal brackets depends on the specific requirements of the application. Some common materials include:
– Steel: Known for its strength and durability, steel is often used for heavy-duty applications that require high load-bearing capacity.
– Stainless Steel: This material is highly resistant to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for use in harsh environments, such as marine or outdoor applications.
– Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum is often used for applications where weight is a concern, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
– Brass: Known for its decorative appeal and resistance to corrosion, brass is commonly used in applications that require aesthetic appeal, such as in high-end furniture or electrical fixtures.
– Copper: Copper’s excellent conductivity makes it ideal for use in electrical applications. It is also naturally antimicrobial, making it suitable for medical or food-related applications.
– Titanium: Lightweight yet strong, titanium is used for high-performance applications, including aerospace and military industries, though it is more expensive than other metals.
Surface Treatments for Metal Brackets
To improve their durability, functionality, and appearance, metal brackets often undergo surface treatments. Some common options include:
– Powder Coating: A process in which a dry powder is applied to the bracket’s surface, providing a durable, weather-resistant finish.
– Anodizing: A treatment that increases the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the metal, improving corrosion resistance and surface hardness.

– Electroplating: A process in which a thin layer of metal, such as nickel or zinc, is applied to the bracket’s surface to improve corrosion resistance and enhance appearance.
– Passivation: A chemical treatment that enhances the metal’s natural oxide layer, improving corrosion resistance, especially in stainless steel brackets.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Metal Brackets
When selecting the right metal bracket for your project, several factors should be considered:
– Material Strength: Choose a material that can handle the weight and forces it will be subjected to.
– Corrosion Resistance: Consider how well the material resists rust and degradation, especially if the bracket will be exposed to the elements.
– Load Capacity: Ensure the bracket is capable of supporting the weight and forces required for your application.
– Bending Angle: The bracket’s angle must provide the necessary support and stability.
– Size and Shape: Make sure the bracket fits the intended application, whether it’s an L, T, or U shape.
– Mounting Holes: Ensure the bracket has the appropriate holes for easy installation.
– Cost: Find a balance between quality, strength, and affordability.
In Conclusion
At Topmetalstamping, we understand the importance of choosing the right metal bracket for your project. With our expertise in manufacturing high-quality custom metal brackets, we are committed to delivering durable, reliable, and precisely engineered solutions tailored to your specific needs. Whether you’re working on small-scale furniture projects or large industrial applications, we offer a range of materials, finishes, and designs to ensure you get the perfect bracket for your needs. Contact us today to learn how we can support your next project with precision-crafted metal brackets that deliver exceptional performance and durability.



