Dies are essential tools in the manufacturing industry, widely used for producing custom parts and components in high-volume production environments. Whether it’s the creation of automotive parts, electronics enclosures, or consumer goods, dies help manufacturers achieve precision, consistency, and efficiency in their processes. But what exactly are dies, how do they work, and what makes them indispensable in modern manufacturing? This article takes a closer look at the role of dies, the different types of die manufacturing processes, and their importance in industrial applications.
What Is a Die in Manufacturing?
In simple terms, a die is a specialized tool used in manufacturing to cut, shape, or form raw materials such as metal, plastic, rubber, or composites into a desired shape or size. Dies are typically used in conjunction with a press, which applies significant force to the raw material to force it into the die’s cavity. The result is a part that precisely matches the dimensions and shape of the die itself.
A die is typically custom-made for a particular application or manufacturing process, designed to fit the specifications required by the product being created. This allows manufacturers to produce parts in a consistent, repeatable manner. Dies can be used to create a wide range of parts, from small fasteners to large automotive components and everything in between.
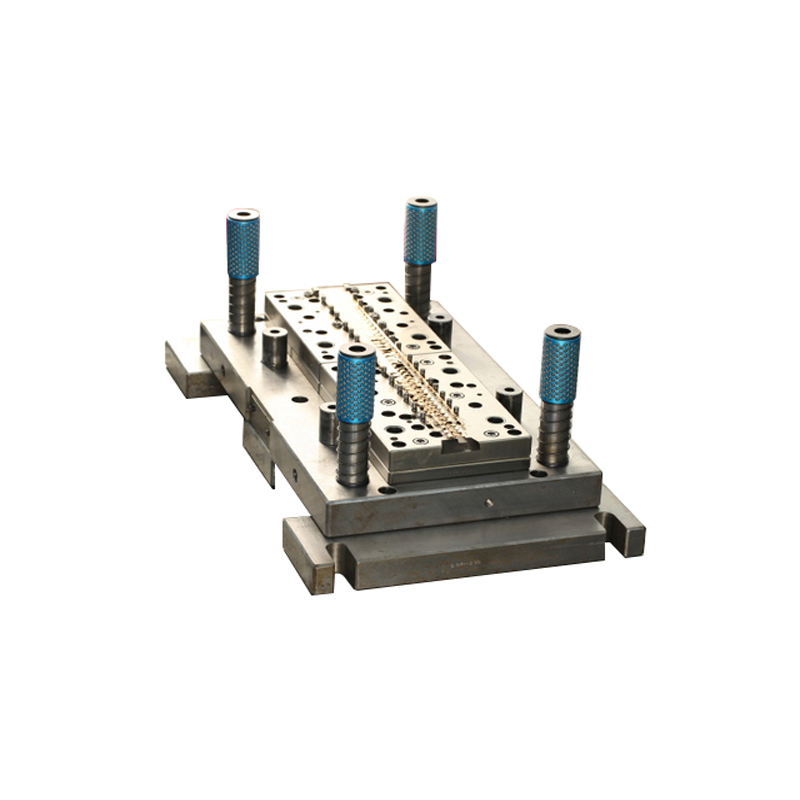
How Do Dies Work?
The process of using a die in manufacturing is often referred to as “die stamping” or “die forming.” The raw material, typically a flat sheet of metal or plastic, is placed into a press. The press then applies force, pushing the material into the cavity of the die. The die’s cavity is shaped in the form of the desired part, so as the material is forced into the die, it adopts the shape of the cavity.
There are several types of processes that rely on dies to create the desired shapes and products. These include:
- Blanking – In this process, a die is used to cut a flat piece of material (such as sheet metal) into a desired shape or blank, which can then be further processed into final products.
- Coining – A die is used to apply high pressure to a piece of metal to produce a finished shape with intricate designs, logos, or features like texturing or embossing.
- Deep Drawing – A die is used to stretch and form a flat sheet of material into a deeper, hollow shape, commonly used in the production of beverage cans, automotive parts, and other deep-well products.
- Piercing and Punching – Dies are used to create holes or cutouts in the material. This process is commonly used to create holes in metal parts for bolts, screws, or wiring.
- Forming – Dies are used to shape the material through bending or forming without necessarily cutting it. This is often used in the production of complex shapes that cannot be easily blanked.
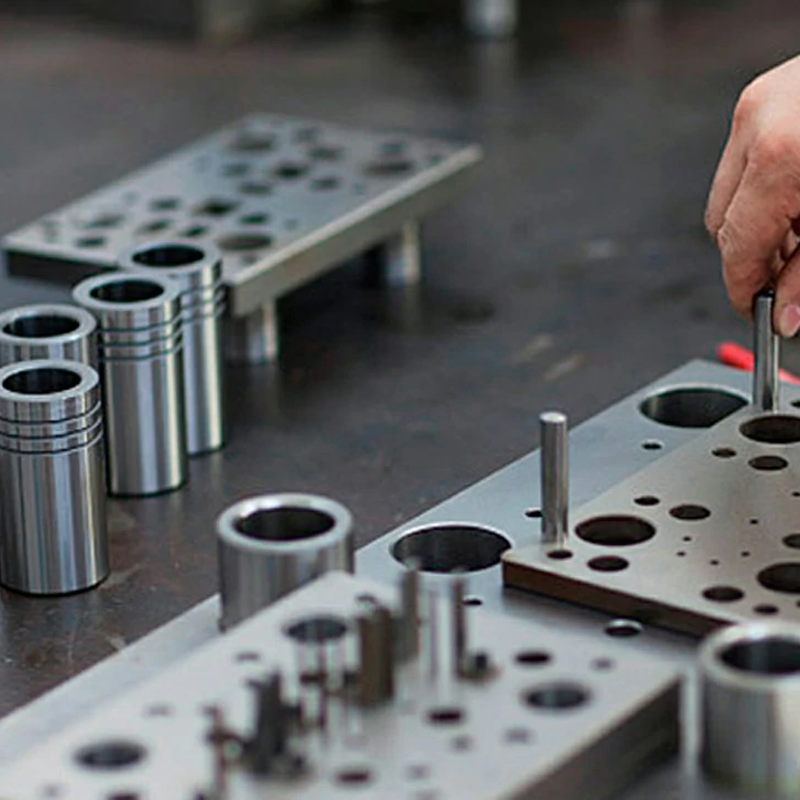

The Parts of a Die Set
A die set typically includes several parts that work together to form a complete tooling system. These components vary depending on the specific type of die being used and the application, but common parts include:
- Punch Plate – The punch plate holds the punch and helps guide it through the material during the forming process.
- Die Block – This is the core component of the die, which contains the cavity that shapes the material.
- Blank Punch – This is the tool used to cut the raw material into a blank, the initial piece that will later be shaped or further processed.
- Pierce Pinch – A tool used to punch holes or create slots in the material.
- Shank – The part of the die that connects the tool to the press.
- Dowel Pin – These are used to align the die set parts to ensure consistent operation.
- Pierce Punch – The punch used to make specific holes or cuts in the material.
- Pilot – A tool used to precisely guide the material into the die set.
- Stripper Plate – A plate that removes the part from the die after it is formed.
Each of these parts has a specific role in ensuring the die operates correctly, and they must be designed and manufactured with high precision to ensure the die works efficiently in production.

Dies vs. Molds: Understanding the Difference
While dies and molds may seem similar because both are used to shape materials, they are quite different in terms of their operation and applications.
– Molds – Molds are typically used in processes where a material is poured into a hollow cavity, often when dealing with materials like plastics or rubber. The material cools and solidifies inside the mold, taking on its shape.
– Dies – In contrast, dies use mechanical force to shape the material. The material is typically in solid form when it is placed into the die, and the die’s force is used to cut, stamp, or form the material into the desired shape.
While both tools are used for shaping materials, dies are commonly used in processes like stamping, punching, and cutting, while molds are generally used in casting and injection molding.
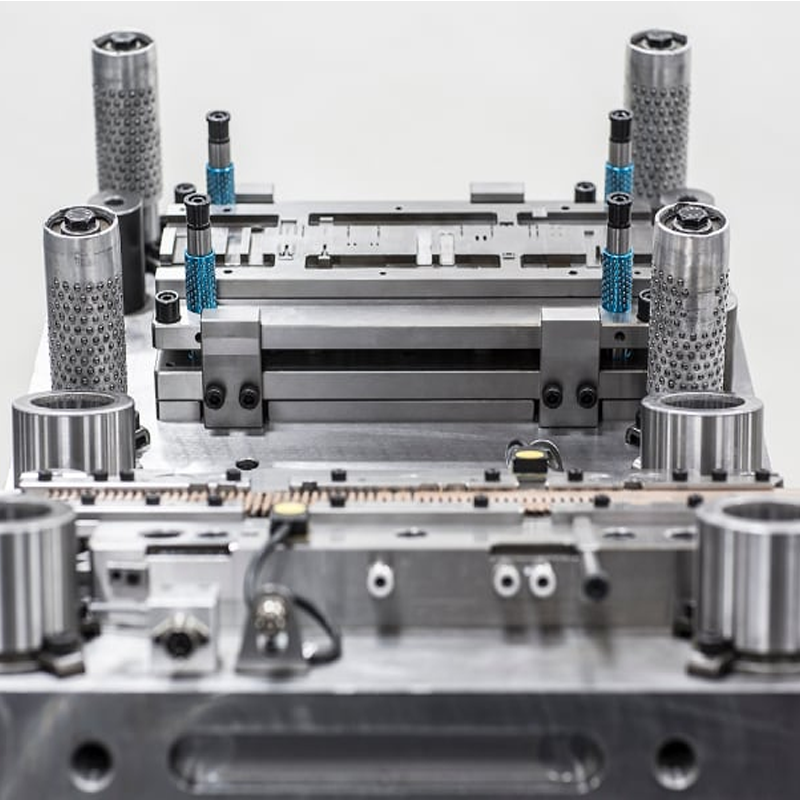
Key Manufacturing Processes That Use Dies
Dies are critical tools in a wide range of manufacturing processes, and their applications are varied across industries. Some of the most common processes that involve dies include:
- Metal Stamping – Metal stamping is one of the most common uses of dies. In this process, dies are used to cut, shape, and form metal sheets into a variety of parts used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
- Injection Molding – Dies are used in the injection molding process to create precise plastic parts by injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity.
- Sheet Metal Forming – Dies are used in sheet metal forming processes such as bending, coining, and deep drawing to create complex shapes in thin metal sheets, commonly used in the automotive and consumer electronics industries.
- Cold and Hot Forging – Dies are used in forging processes to shape metal at high temperatures (hot forging) or at room temperature (cold forging) by applying immense pressure to form parts like gears, shafts, and bolts.
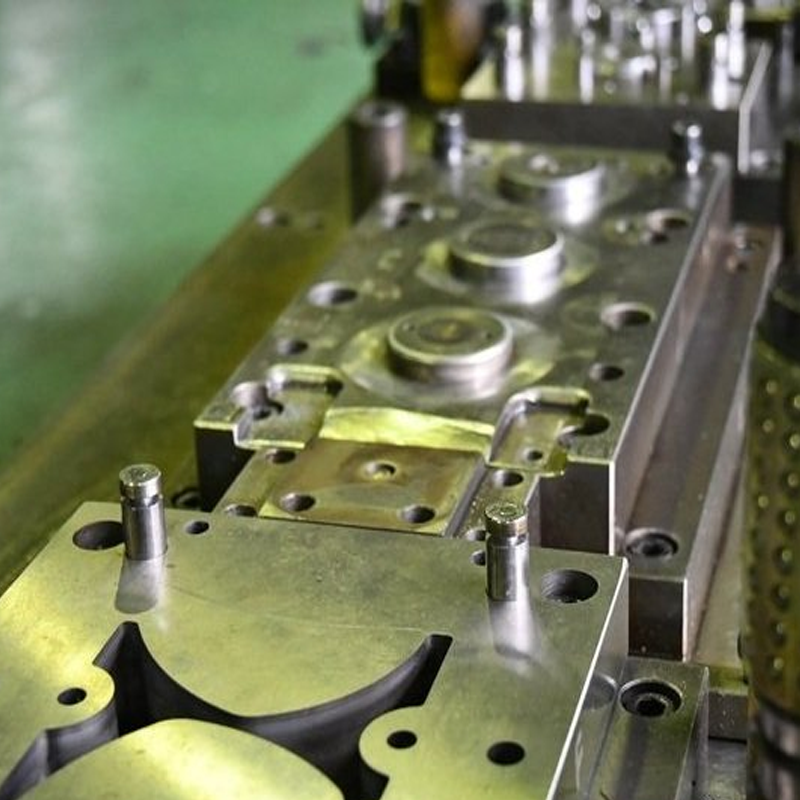

The Benefits of Using Dies in Manufacturing
There are several advantages to using dies in manufacturing, particularly for high-volume production runs. Some of the key benefits include:
– Precision and Consistency – Dies allow for the production of parts with high precision and consistency, ensuring that each part meets the same specifications.
– Speed and Efficiency – Once the die is made, it can be used repeatedly to produce large volumes of parts, significantly increasing the efficiency of the manufacturing process.
– Cost-Effectiveness – For high-volume production, custom dies can help reduce costs over time, as they enable manufacturers to create parts faster and with less waste.
– Complex Geometries – Dies are capable of producing parts with intricate shapes and features, making them ideal for complex products that cannot be easily produced by other methods.
Conclusion
Dies are indispensable tools in the modern manufacturing process. By utilizing dies, manufacturers can produce a wide range of parts with high precision, efficiency, and consistency. Whether used in metal stamping, injection molding, or sheet metal forming, dies help businesses meet the increasing demands for quality and cost-effectiveness in production.

If you’re looking for a reliable partner to handle your die-related manufacturing needs, or you’re interested in seeing how dies are used to create custom parts, don’t hesitate to contact us today. Our experienced engineers and production team can help guide you through the process, ensuring your parts are manufactured to the highest standards of quality.



