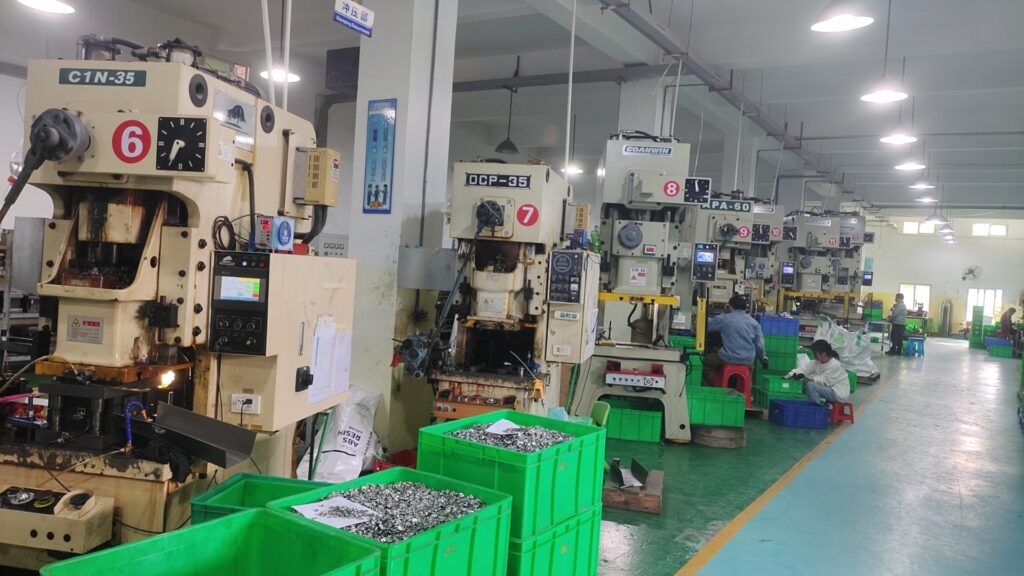
A computer’s CPU (central processing unit) is highly susceptible to overheating due to the intense thermal output from certain components, which can jeopardize the system’s overall performance.
In this blog, we will explore how heat sinks play a crucial role in safeguarding your CPU from excessive heat, ensuring optimal efficiency and preserving the integrity of vital components.
A computer’s Central Processing Unit (CPU) is one of the most critical components in a system, responsible for executing instructions and handling the tasks that make your computer run smoothly. Due to the high workload and electrical activity within the CPU, it generates a significant amount of heat. Without proper heat management, this excess heat can cause the CPU to overheat, leading to decreased performance or even hardware failure.
In this article, we’ll discuss the role of a heat sink, how it works, the types of heat sinks available, and why it’s vital to have an efficient cooling system for your computer’s CPU to maintain its performance and longevity.
What is a Heat Sink?
A heat sink is a specialized piece of metal, typically made from high-conductivity materials like aluminum or copper, that sits on top of a computer chip—most commonly a CPU or GPU. Its primary function is to absorb heat from these components and dissipate it into the surrounding environment. Heat sinks are designed with fins or ridges to maximize surface area, allowing heat to be transferred more efficiently.
Heat sinks are inherently passive devices, meaning they have no moving parts and rely on natural convection to move heat away from the CPU. However, to improve heat dissipation, most modern systems combine heat sinks with active cooling solutions, such as fans or liquid cooling systems, which help remove heat more rapidly.
The Purpose of a Heat Sink
As CPUs continue to become more powerful, they produce more heat. If not properly managed, this heat can cause the CPU to overheat, potentially leading to serious hardware damage. Electronic components are particularly sensitive to temperature fluctuations, and prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause permanent damage to delicate circuits, rendering the component useless.
A heat sink ensures that heat is efficiently transferred away from the CPU, keeping the temperature within safe operating limits. By dissipating heat effectively, the heat sink helps maintain the CPU’s performance and prevents thermal throttling—when the CPU slows down to reduce heat production, which negatively impacts performance.
Additionally, having an effective heat sink in place allows the CPU to operate continuously under heavy workloads, such as gaming, video editing, or running demanding software applications, without the risk of overheating.
How Does a Heat Sink Work?
The heat sink performs its job in four essential steps:
- Heat Generation: The CPU or GPU generates heat as it processes data. This heat must be dissipated to prevent overheating.
- Heat Transfer: The heat generated by the CPU is transferred into the heat sink through direct contact. A thermal interface material (TIM), such as thermal paste or thermal compound, is often applied between the CPU and the heat sink to fill in any microscopic gaps and ensure efficient heat transfer.
- Heat Distribution: Once the heat is absorbed by the heat sink, it spreads throughout the fins or other parts of the heat sink’s structure. The heat moves naturally from areas of high temperature (near the base) to areas of lower temperature (at the tips of the fins) through conduction.
- Heat Dissipation: The heat is then dissipated into the surrounding air. This process can be further enhanced by using a fan to force air over the heat sink’s fins or through a liquid cooling solution that carries heat away from the CPU. The larger the surface area of the heat sink, the more effectively it can dissipate heat.
Types of Heat Sinks
There are three primary types of heat sinks used in modern computers:
-
Passive Heat Sinks:
Passive heat sinks rely solely on natural convection to disperse heat. Since they do not have moving parts or require external power, they are often quieter and more reliable over long periods. However, they are less effective at cooling compared to active heat sinks, especially in systems where the CPU is under heavy load.
-
Active Heat Sinks:
Active heat sinks include additional cooling components, such as fans or liquid cooling systems, to actively move heat away from the CPU. By increasing airflow over the heat sink’s fins, active heat sinks can remove heat more quickly and maintain lower CPU temperatures. This type of heat sink is common in high-performance systems where continuous cooling is essential.
-
Hybrid Heat Sinks:
Hybrid heat sinks combine elements of both passive and active cooling. They often use fans that only engage when the CPU reaches a certain temperature, allowing for quieter operation under lighter workloads. Once the CPU reaches higher temperatures, the active cooling system kicks in to prevent overheating. Hybrid systems provide the best of both worlds, offering efficient cooling when needed while reducing noise during low-power tasks.
What is Heat Sink Compound?
Heat sink compound, also known as thermal paste or thermal interface material (TIM), plays a critical role in ensuring effective heat transfer between the CPU and the heat sink. Since no surface is perfectly smooth, microscopic air gaps can exist between the two, reducing heat conductivity. The compound fills these gaps, creating a better thermal connection and allowing heat to flow more efficiently from the CPU to the heat sink.
Applying the right amount of thermal compound is essential for optimal performance. Too much can insulate the CPU, trapping heat, while too little can leave air pockets, reducing heat transfer efficiency.
Why is a Heat Sink Important?
A heat sink is vital to any computer system because it directly impacts the performance and lifespan of your CPU. Without proper heat dissipation, a CPU can quickly overheat, causing thermal throttling or even permanent damage to the processor. Overheating can also lead to other issues, such as data corruption, system crashes, and reduced overall performance.
Moreover, in high-performance systems, such as gaming PCs or workstations used for tasks like video editing or 3D rendering, heat management becomes even more critical. These tasks generate substantial amounts of heat, and without a reliable heat sink in place, the system’s efficiency and stability would be compromised.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Heat Sink
Choosing the right heat sink for your system is crucial to maintaining its optimal performance. The size, material, and type of heat sink you select should depend on your system’s cooling needs. For example:
– Material: Heat sinks made from aluminum are lightweight and affordable, making them ideal for general-purpose systems. Copper heat sinks, on the other hand, have superior thermal conductivity, making them better suited for high-performance systems, though they are heavier and more expensive.

– Surface Area: The more surface area a heat sink has, the better it can dissipate heat. This is why heat sinks are designed with fins or ridges, which increase the surface area and improve heat dissipation.
– Active vs. Passive: If your system runs resource-intensive tasks or operates in a warm environment, an active heat sink with a fan or liquid cooling system may be necessary to prevent overheating. For lighter workloads or systems that prioritize silent operation, a passive heat sink may suffice.

Conclusion
Heat sinks are an indispensable part of a computer’s thermal management system. They protect the CPU from overheating, ensuring consistent performance and extending the lifespan of critical components. By understanding how heat sinks work and the different types available, you can make informed decisions about the cooling solutions best suited for your computer’s needs.
At Topmetalstamping, we provide custom thermal solutions, including high-performance heat sinks and blower fans, to ensure your components remain cool under any conditions. Our engineers meticulously test each system to ensure optimal heat dissipation, guaranteeing that your system performs at its best, even in the most demanding environments. Whether you need a passive, active, or hybrid cooling solution, we have the expertise to help you achieve the best results for your system.




